Currently Empty: R0.00
Reverse Osmosis
- Home
- Reverse Osmosis
Buy Our Wide Range Of RO Water Treatment Systems
Made For Africa
- Best Quality Products
- Training Offered
- Domestic & Industrial
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis is the process of removing dissolved elements from your water. For example, if you have a cup of water. Each time you add a teaspoon of sugar, The TDS will increase. So, the more sugar you add, the higher your tds will be. A filter system will not remove the sugar that’s dissolved in the water. The only way to remove what’s dissolved is the water is to put it through a reverse osmosis system.
Reverse Osmosis is a technology that is used to remove a large majority of dissolved contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. So if you have to put sweet water through the reverse osmosis system, you will have 2 outputs. Your pure water will have no taste (permeate ), and the water water will be more sweet ( concentrate )
How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
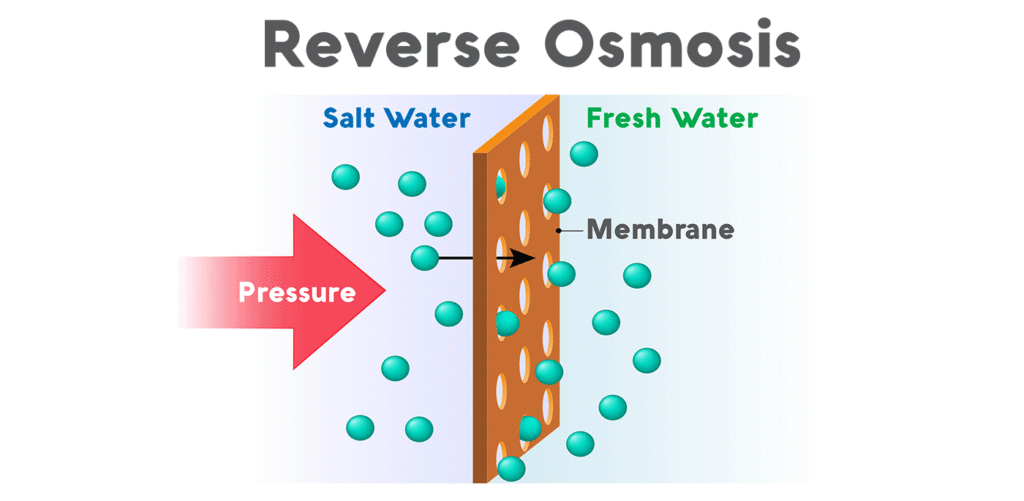
Reverse Osmosis Mebrane
A semipermeable membrane has small pores that block contaminants but allow water molecules to flow through. In osmosis, water becomes more concentrated as it passes through the membrane to obtain equilibrium on both sides. Reverse osmosis, however, blocks contaminants from entering the less concentrated side of the membrane. For example, when pressure is applied to a volume of saltwater during reverse osmosis, the salt is left behind and only clean water flows through.
What does a reverse osmosis system remove In Water?
Sediments
Salts
Herbicides and pesticides
Chlorine
Fluoride
Many other contaminants
Reverse Osmosis is capable of removing up to 99%+ of the dissolved salts (ions), particles, colloids, organics, bacteria and pyrogens from the feed water (although an RO system should not be relied upon to remove 100% of bacteria and viruses). An RO membrane rejects contaminants based on their size and charge. Any contaminant that has a molecular weight greater than 200 is likely rejected by a properly running RO system (for comparison a water molecule has a MW of 18). Likewise, the greater the ionic charge of the contaminant, the more likely it will be unable to pass through the RO membrane. For example, a sodium ion has only one charge (monovalent) and is not rejected by the RO membrane as well as calcium for example,
which has two charges. Likewise, this is why an RO system does not remove gases such as CO2 very well because they are not highly ionized (charged) while in solution and have a very low molecular weight. Because an RO system does not remove gases, the permeate water can have a slightly lower than normal pH level depending on CO2 levels in the feed water as the CO2 is converted to carbonic acid. Reverse Osmosis is very effective in treating brackish, surface and ground water for both large and small flows applications. Some examples of industries that use RO water include pharmaceutical, boiler feed water, food and beverage, metal finishing and semiconductor manufacturing to name a few.
The advantages of Reverse Osmosis
RO systems help remove impurities in the water and leave you with a refreshing and great-tasting water. Critical filtration steps have to be taken before the purification of the water.
- Clean and clear water is the key to a better health
- We are here to help with whatever you need to know about Water Purification
- All the technical support you need based on our products
- Starting a water business has never been so easy